Acute Kidney Injuries
This will be a review of causes of acute kidney injuries, diagnostic criteria (RIFLE and AKIN), indications for hemodialysis, and types of dialysis.
Our final ICU topic (for now) will be acute kidney injuries (AKI)! It seems like almost everyone in the ICU has an AKI - and that’s because around 70% of ICU patients have some degree of renal dysfunction.
Once you suspect a kidney injury, you can divide the possible causes into 3 broad categories: pre-renal, intra-renal, and post-renal. Pre-renal disease is associate with decrease renal blood. This accounts for 30-40% of AKIs. You can quickly rule out pre-renal disease by looking at certain urine measurements.
Intra-renal disease usually is due to two possible causes - acute tubular necrosis (ATN) or acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) - depending on where the insult is. ATN accounts for 50% of AKIs and is always secondary to some larger insult like septic shock, nephrotoxic agents, or rhabdomyolysis.
Post-renal disease refers to some sort of blockage at the level of the renal collecting ducts, ureters, or urethra. This accounts for 10% of AKIs.
There are two competing criteria that attempt to classify the presence and severity of a kidney injury - the RIFLE and AKIN Criteria. They both take into account serum creatinine (compared to the patient’s baseline) and urine output over time. The two sets of criteria are equivalent in predicting mortality rates.
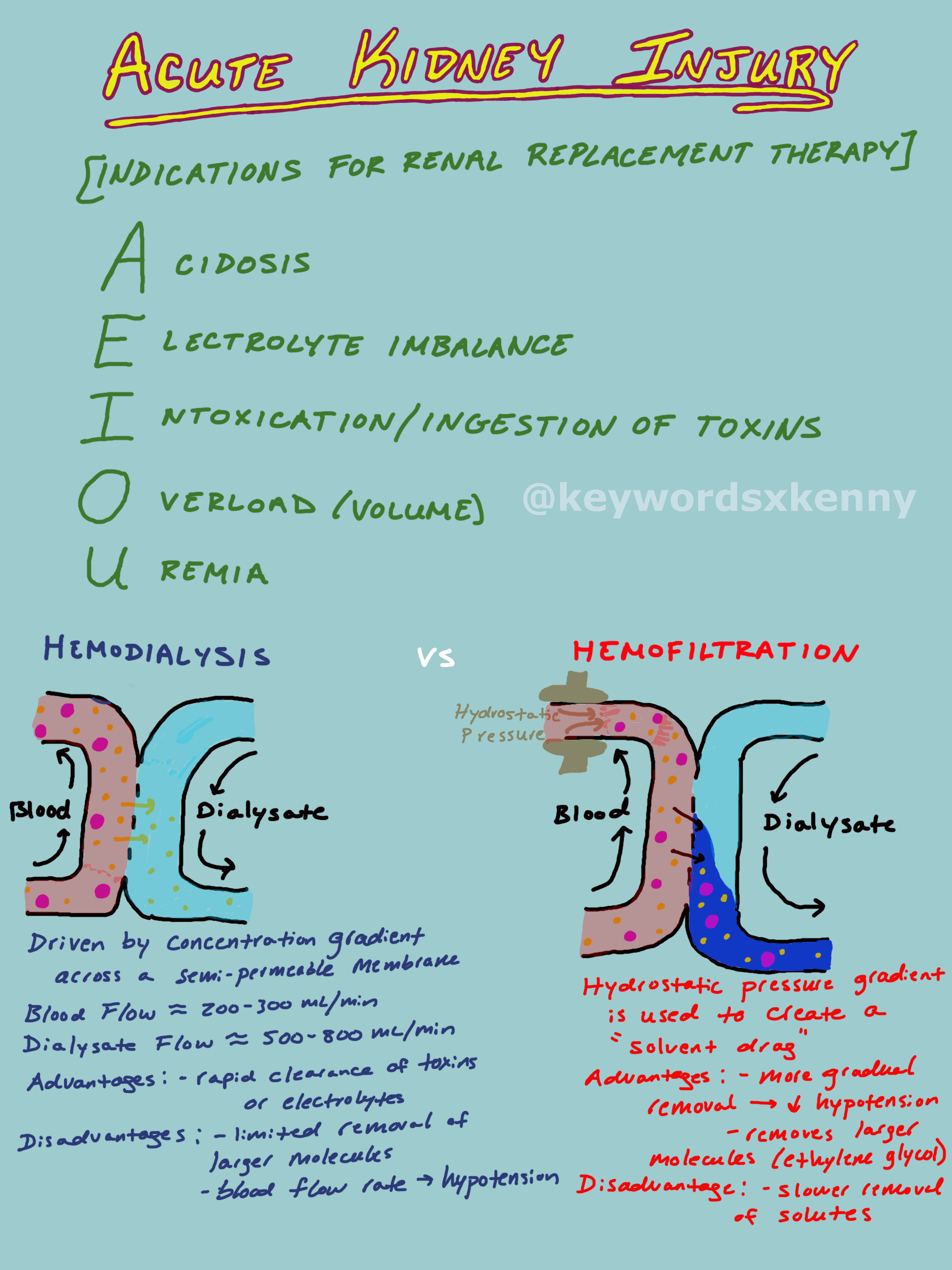
The last thing to keep is mind is when to initiate renal replacement therapy. The indications for RRT can be remembered with the mnemonic “AEIOU” - Acidosis, Electrolyte imbalance, Intoxication/Ingestion, Overloaded with fluid, and Uremia. RRT therapy comes in two flavors - hemodialysis and hemofiltration. Hemodialysis uses a concentration gradient to remove solvents from the blood where as hemofiltration uses hydrostatics pressure to create a solvent drag across the membrane. The major advantages of hemodialysis is it can work fast to remove toxins/electrolytes with the major downside of hypotension created by the blood flow needed to run the machine. The major advantage of hemofiltration is that you have less hypotension slowly removing solvent and you can remove large molecules such as ethylene glycol and inflammatory cytokines.